Executive summary VDY vs XEI
When contemplating between VDY and XEI, the decision hinges on your investment goals. VDY emphasizes dividend yield, drawing from high-quality Canadian stocks, though it faced challenges due to a banking sector retreat. On the other hand, XEI, with a passive strategy, showcases resilience through the strength of the energy sector. Consider your risk tolerance and investment objectives—consistent growth or robust dividends. While VDY leans towards the latter, be mindful of its heavy exposure to the financial sector. In contrast, XEI offers a more stable trajectory. Weigh the nuances outlined to align your investment strategy with your financial objectives.

VDY:
VDY is a popular Canadian dividend ETF, offering instant exposure to a high-quality portfolio of high dividend-paying stocks. This Canadian-focused ETF aims to replicate the performance of the FTSE Canada High Dividend Yield Index, which comprises Canadian stocks with a high dividend yield. Managed by FTSE, a global leader in index creation, the index follows a meticulous process. It selects companies from the broad Canadian equity index (FTSE Canada Index) and evaluates their 12-month forward dividend yield using Thomson Reuters’ I/B/E/S. Stocks forecasted to pay no regular dividends in the next 12 months are excluded. The index then ranks and periodically screens for liquidity. In examining VDY’s objective, strategy, volatility, and performance, this post also delves into a comparison with rival ETFs, providing investors with a comprehensive overview of VDY stock in the Canadian dividend landscape.
XEI:
XEI ETF, managed with a passive strategy, aims to replicate the performance of the S&P/TSX Composite High Dividend Index ETF. Ideal for investors seeking long-term capital growth, XEI provides exposure to diversified sectors of Canadian companies. The ETF offers a monthly dividend income, catering to investors desiring frequent payouts. The S&P/TSX Composite High Dividend Index, comprised of 50 to 75 stocks, focuses on dividend income, with constituent issuer weights limited to 5% and sector weights capped at 30%. Managed by Standard & Poor’s, the index considers criteria like market capitalization, liquidity, and domicile on the Toronto Stock Exchange. Rebalanced quarterly, it ensures alignment with its objectives and provides geographic and economic balance across 11 GICS® sectors.
Performance comparison VDY vs XEI
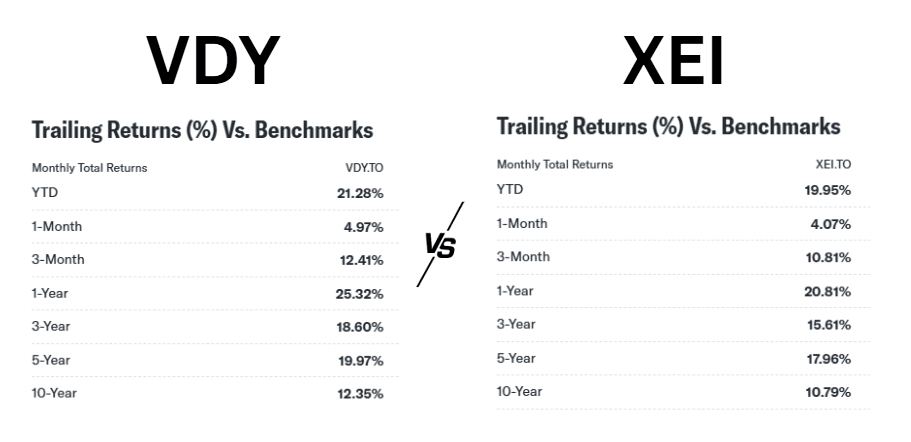
VDY vs XEI: Full comparison

Objective and Strategy:
VDY, focusing on high-quality Canadian dividend stocks, replicates the FTSE Canada High Dividend Yield Index using a meticulous selection process. Meanwhile, XEI adopts a passive strategy, tracking the S&P/TSX Composite High Dividend Index ETF to provide exposure to diversified sectors of Canadian companies. Both ETFs aim to meet investors’ objectives, with VDY emphasizing high dividend yield and XEI targeting long-term capital growth.
Volatility and Performance:
VDY’s approach involves evaluating 12-month forward dividend yield, excluding stocks forecasted to pay no dividends. XEI, on the other hand, follows criteria such as market capitalization, liquidity, and domicile to ensure alignment with its objectives. Both strategies contribute to overall performance, with VDY emphasizing quality and dividend yield, while XEI offers exposure to a broad market with a focus on high dividends.
VDY.TO, despite its historical strong performance, faced headwinds at the start of the year due to a retreat in the big Canadian banking sector. The negative impact on VDY’s YTD return of -4.56% can be attributed to the significant influence of banking stocks in its portfolio. The retreat is likely associated with the rise in interest rates, a factor that tends to impact banking stocks negatively.
On the other hand, XEI.TO has displayed better performance YTD, with a positive return of 0.21%, mainly attributed to the resilience of the energy sector. The positive performance of the energy sector has acted as a buffer, mitigating the overall impact of sector-specific challenges faced by VDY.
Fees:
In terms of fees, both ETFs are tied, with an identical Management Expense Ratio (MER) of 0.22%. Vanguard, managing VDY, has a reputation for prioritizing investors and has a track record of lowering fees on their ETF lineup.
High Dividend ETF Duel: Analyzing HMAX vs BKCL
Best High-Interest Savings Account ETFs In Canada
10 Best Covered Call ETF Canada – Boost you income!
Size:
A crucial factor in ETFs is their size, influencing liquidity and trading dynamics. Both XEI and VDY have similar Assets Under Management (AUM) of approximately $1.76 billion and $1.77 billion, respectively, indicating sufficient size for buy-and-hold investors.
Holdings:
XEI tracks the S&P/TSX Composite High Dividend Index with 75 stocks, primarily concentrated in energy, financials, telecommunications, and utilities. VDY tracks the FTSE Canadian High Dividend Yield Index with 39 stocks, concentrated in financials, energy, telecommunications, and utilities. The distribution yields for XEI and VDY are close.
Conclusion
Personally, I lean towards VDY due to its emphasis on high-quality dividend stocks. However, I am mindful of its heavy exposure to the financial sector during portfolio allocation. This awareness allows for a balanced approach, considering both the strengths and potential challenges associated with VDY’s specific sector concentration.
The choice between VDY and XEI depends on investors’ preferences and objectives. VDY’s emphasis on dividend yield may appeal to income-focused investors, while XEI’s broad exposure and resilience in specific sectors may attract those seeking long-term growth.
Portfolio holdings
VDY ETF holdings
| Holding Name | % of Market Value |
|---|---|
| Royal Bank of Canada | 13.86% |
| Toronto-Dominion Bank | 12.62% |
| Enbridge Inc. | 7.46% |
| Bank of Nova Scotia | 7.45% |
| Bank of Montreal | 6.63% |
| Canadian Imperial Bank of Commerce | 4.80% |
| Canadian Natural Resources Ltd. | 4.67% |
| TC Energy Corp. | 4.51% |
Please refer to issuers’ website for the most up-to-date data
XEI ETF holdings
| Name | Weight (%) |
|---|---|
| CANADIAN NATURAL RESOURCES LTD | 5.72 |
| NUTRIEN LTD | 5.39 |
| TC ENERGY CORP | 5.12 |
| ENBRIDGE INC | 5.03 |
| TORONTO DOMINION | 5.02 |
| SUNCOR ENERGY INC | 4.85 |
| ROYAL BANK OF CANADA | 4.83 |
| BCE INC | 4.62 |
| BANK OF NOVA SCOTIA | 4.43 |
| TELUS CORP | 4.18 |
- DGS ETF Explained: How Dividend Growth Split Corp Really Works — and the Risks Most Investors Miss
- Best Hamilton ETFs for Monthly Income in 2026 (High Yield, Covered Call ETFs)
- HHIS ETF Review: Harvest Diversified High Income Shares Explained
- JEPI vs QYLD: The Ultimate Covered Call Income Battle
- Best U.S. Covered Call ETFs (2026): High Income, Explained Clearly
- Best Covered Call ETF Canada – Boost you income!
